A field effect transistor (FET) is an important and commonly used electronic component found throughout several areas of the electronics industry, including integrated circuits.
Integrated circuits using FETs consume much less power than integrated circuits using bipolar transistor technology, and this means they can be used on a much larger scale.
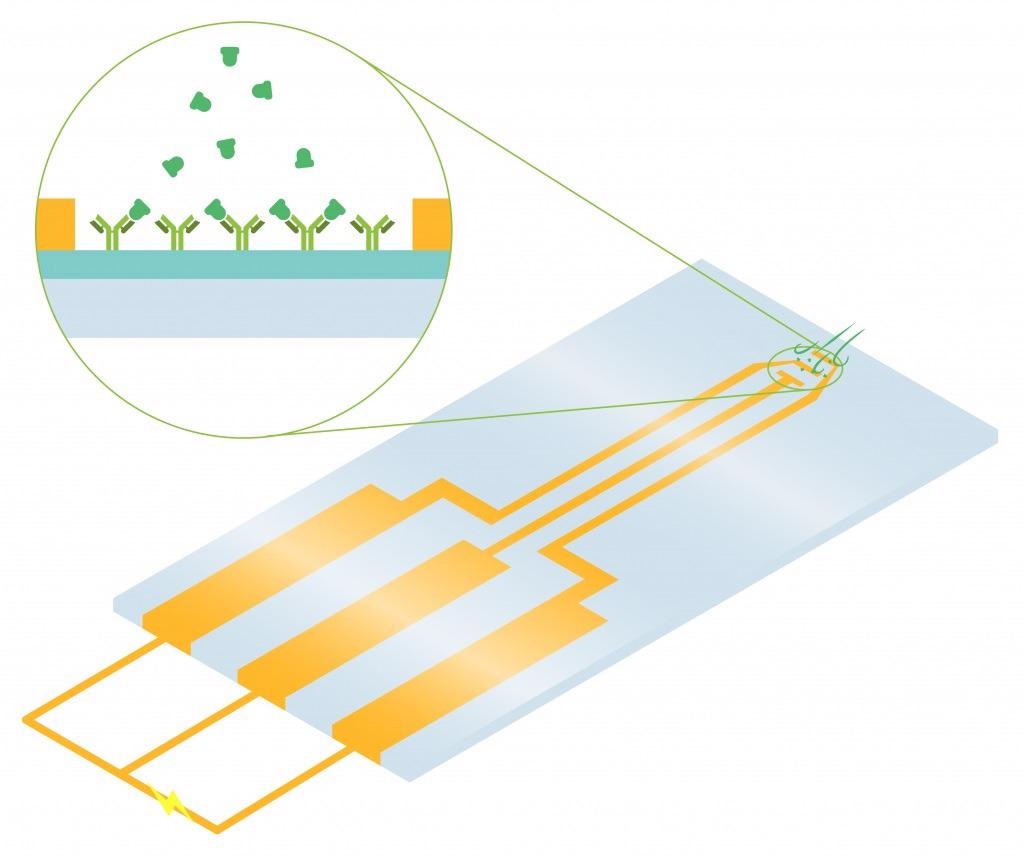
Image Credit: Platypus Technologies, LLC
FETs work on the principle that charge on an object close by is able to attract charges within a semiconductor channel. This generally operates using an electric field, hence FETs’ name. FETs are made up of a semiconductor channel that has electrodes at each end. The electrodes are referred to as the drain and the source.
A FET gate is a control electrode placed near the channel, allowing its electric charge to impact the channel. The FET gate manages the flow of carriers from source to drain by controlling the conductive channel’s size and shape.
What are Biosensor Chips?
Biosensors are analytical devices suitable for the detection of chemical substances. They do this by combining a biological component with a physicochemical detector. Biosensor chips are comprised of several distinct biosensors, and these sensors can be monitored separately and used to analyze a range of analytes.
The role of transducers is essentially the translation of information from biosensors, for example, the effects of interactions. This information is then converted into a measurable effect like an electrical signal. Biosensor chips are generally classified according to their bioreceptor or transducer type.
Understanding Biosensor Chips Based on FET
A FET-based biosensor chip will employ a FET that is gated by alterations in the surface potential prompted by the binding of molecules.
When charged molecules (for example, biomolecules) successfully bind to the FET gate, they are able to alter the charge dispersal of the underlying semiconductor material. This process triggers a change in the FET channel’s conductance.
FET-based biosensor chips are commonly used by researchers in drug screening and early biomarker detection. These biosensor chips feature non-metalized gate dielectrics, which are exposed to an electrolyte. This covers the semiconductor material, actively transducing the biological alterations occurring on the surface.
FET-based biosensor chips offer extremely efficient real-time detection of different biomolecular analytes. They are also extremely accurate, specific and able to function in a label-free manner.
Numerous studies have verified these benefits, and recent years have seen considerable progress made towards developing FET devices specifically designed for biomedical diagnosis and cell-based assays.
Biosensor chips based on FET also offer outstanding electronic properties while being compact and highly scalable. These qualities make them an ideal solution for rapid, label-free and mass biomolecule detection.
The performance of biosensor chips based on FET is significantly increased when these are incorporated with nanotechnology. This is particularly the case when they are used with nanomaterials such as metal nanoparticles, graphene, single and multi-walled carbon nanotubes, nanowires, and nanorods.
In addition to this array of benefits, high quality biosensor chips based on FET are widely available on a commercial basis, resulting in them being one of the most favored sensing and screening platforms.

This information has been sourced, reviewed and adapted from materials provided by Platypus Technologies, LLC.
For more information on this source, please visit Platypus Technologies, LLC.