May 8 2024Reviewed by Lexie Corner
Chi Hwan Lee and his colleagues developed a smart neckband that tracks eating and drinking habits. This machine-learning-powered device uses sensors to distinguish between these actions and similar movements like talking and walking, offering the potential for managing diabetes and improving overall health. The study was published in the journal PNAS Nexus.
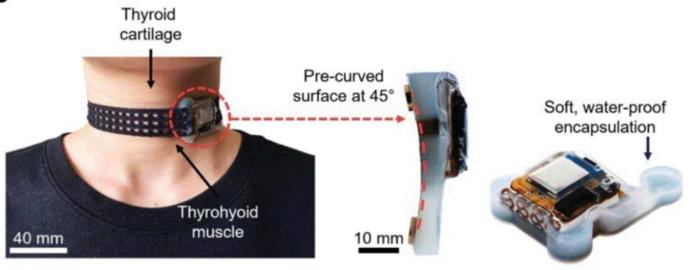 The sensor module, positioned on the thyrohyoid muscle, features a 45-degree pre-curved design and soft, waterproof encapsulation. Image Credit: Park et al.
The sensor module, positioned on the thyrohyoid muscle, features a 45-degree pre-curved design and soft, waterproof encapsulation. Image Credit: Park et al.
Wearers of smart neckbands can monitor how much food they consume. When maximizing fitness or managing illnesses like diabetes and obesity, automatically tracking food and hydration intake might be helpful. However, eating and drinking must be distinguished from related motions like speaking and walking via wearable technology.
Chi Hwan Lee and colleagues propose a neckband with machine learning capabilities that can distinguish between speech, body language, hydration, and food intake. The neckband's sensor module includes a microphone, a three-axis accelerometer, and a surface electromyography sensor.
Combined, these sensors can record auditory data, body motions, and muscular activation patterns in the neck's thyrohyoid muscle. With an accuracy rate of almost 96 % for individual activities and 89 % for concurrent activities, the machine-learning algorithm accurately identified which movements in research involving six participants were related to eating or drinking.
Made of breathable, mesh-structured, flexible, and twistable cloth, the neckband has 47 active and passive components that can operate on battery power for over 18 hours without recharging.
The neckband can help athletes and other people interested in improving their general health and wellness. It can also be used in a closed-loop system with a continuous glucose meter and an insulin pump to help diabetic patients determine when to take their insulin dosages.
Journal Reference:
Park, T., et al. (2024) A machine-learning-enabled smart neckband for monitoring dietary intake. PNAS Nexus. doi.org/10.1093/pnasnexus/pgae156.
Source: https://academic.oup.com/pnasnexus