Methane is a potent greenhouse gas released at different stages of gas and oil operations, from upstream to downstream. The impact of methane on climate change was more than 25 times greater than that of carbon dioxide over a period of 100 years, meaning it is a substantial contributor to the climate crisis.

Image Credit: Cubic Sensor and Instrument Co. Ltd
Many nations have set stricter regulations to meet the goal of reducing methane emissions by at least 30% below 2020 levels by 2030.
These regulations include the UN OGMP2.0, EPA Methane Emissions Reduction Plan, and EU Fit for 55, which require more accountability and transparency from the industry regarding methane emissions measurement.
As a result, the detection, localization, and quantification of methane leaks are becoming increasingly important in helping mitigate methane emissions in the gas and oil industry.
Cubic is a manufacturer of gas sensors and gas analyzers with a broad range of diverse industrial solutions for detecting and managing methane emissions, with over 20 years of R&D dedication and accumulation.
To meet the growing demand for methane detection in the gas and oil industry, Cubic has adopted diverse mature technology platforms of non-dispersive infrared (NDIR), tunable diode laser absorption spectroscopy (TDLAS), and Laser Raman technologies to develop superior, reliable, and credible real-time methane gas sensors and analyzers, aiming to reduce methane emissions and improve the reliability and credibility of methane emissions data in the oil and gas industry from upstream to downstream.
This article presents Cubic’s recent technical innovations for the detection of methane in the gas and oil industry.
Non-Dispersive Infrared (NDIR) Sensing Technology
NDIR technology is based on the principle that certain gases absorb infrared light at characteristic wavelengths. Based on NDIR technology, Cubic has developed the miniature low-power NDIR CH4 sensor, SJH series, which can detect between 0% and 5% volume of methane (CH4) concentration.
The low power consumption design enables it to be applied to scenarios that require optimal energy efficiency, battery-powered portable or wearable detectors.
SJH series could facilitate a continuous working current as low as 1 mA and achieve ampere level via a flexible intermittent working model.
Additionally, SJH series maintains an excellent performance for high accuracy over the entire temperature range and has long-term stability due to a matrix calibration mechanism and a dual beam design.
In drilling, pipeline, and oil and gas storage facilities, Cubic NDIR methane sensor- SJH series delivers real-time data, allowing a rapid response to methane leaks to achieve reliable and precise industrial safety alarms.
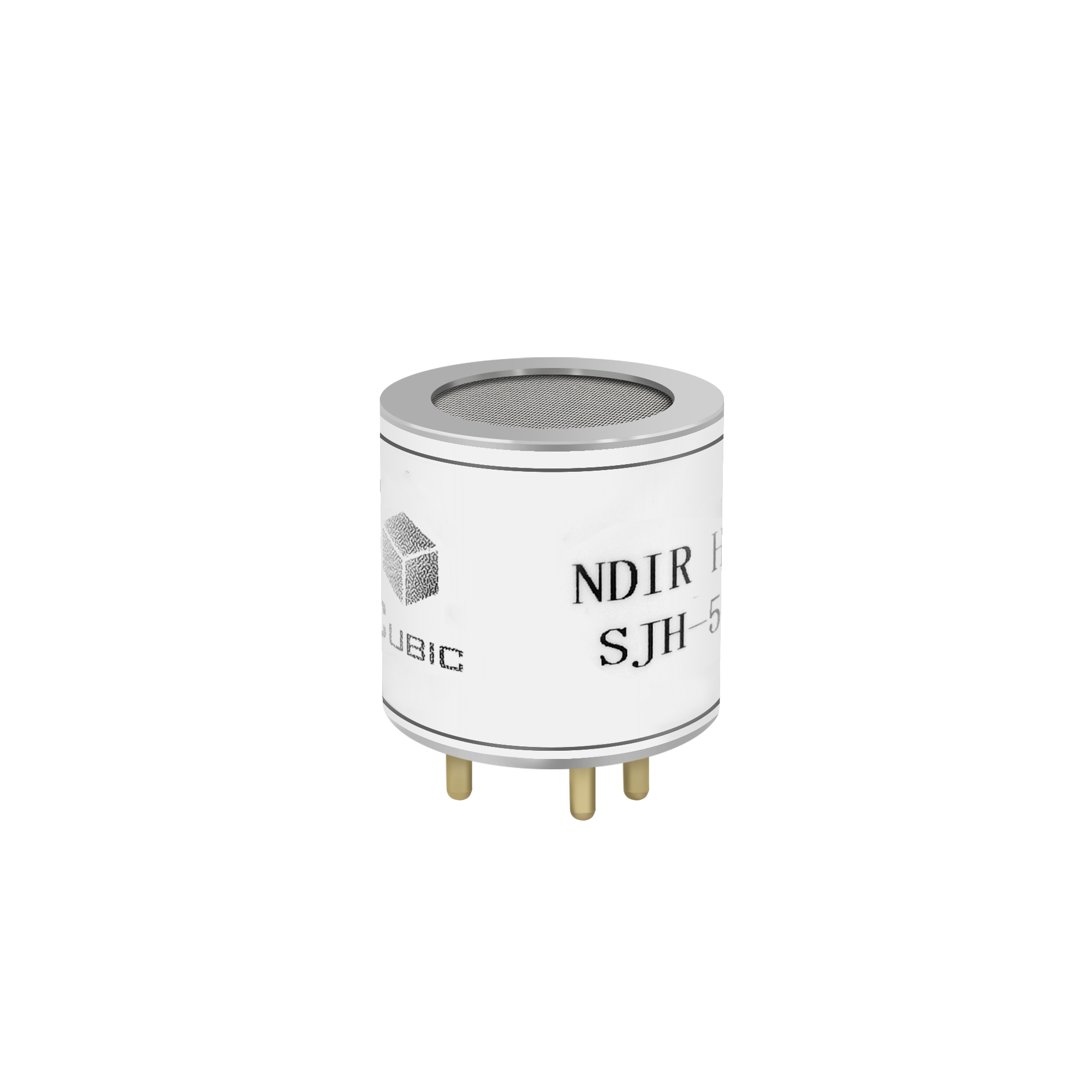

Image Credit: Cubic Sensor and Instrument Co. Ltd
Tunable Diode Laser Absorption Spectroscopy Sensing Technology
Tunable diode laser absorption spectroscopy (TDLAS) sensing technology utilizes the light source of a tunable-wavelength diode laser and a photodiode for detecting light signals.
The wavelength of the diode laser emission is scanned over the absorption peak of the target gas, and the photodiode is employed to detect the light signal after absorption by the target gas, then an absorption spectrum is obtained, which can be used to obtain target gas concentration by further analysis and calculation.
The Cubic methane gas sensor, Gaboard-2502, adopts the TDLAS principle and has been designed with a long optical path for multiple light reflections, enabling the sensor to realize an ultra-low detection limit along with a high resolution in the low concentration range.
The Gasboard-2502 aims to detect low-concentration methane leakage in the atmospheric background, with highly selective and accurate detection of methane leakage. It has a minimum detection limit of 1 ppm and a resolution of 0.1 ppm. Additionally, Gasboard-2502 provides rapid response times with a warm-up of less than 10 seconds.
Regarding adaptations for harsh outdoor working conditions and complex environments, the Gasboard-2502 sensor also has superior advantages due to implementation of TDLAS technology for anti-humidity and has an embedded temperature compensation algorithm and a self-diagnosis function for environmental compatibility.
Image Credit: Cubic Sensor and Instrument Co. Ltd
Laser Raman Spectroscopy Sensing Technology
Laser Raman spectroscopy is a spectral gas analysis technology based on gas Raman scattering. By measuring and analyzing the position and intensity of Raman characteristic peaks with a spectrometer, laser Raman detection technology can be used to simultaneously measure multi-component hydrocarbon gases including CH4.
Cubic LRGA-3100 Laser Raman Spectroscopy gas analyzer was developed by Cubic applying the principle of Laser Raman Scattering.
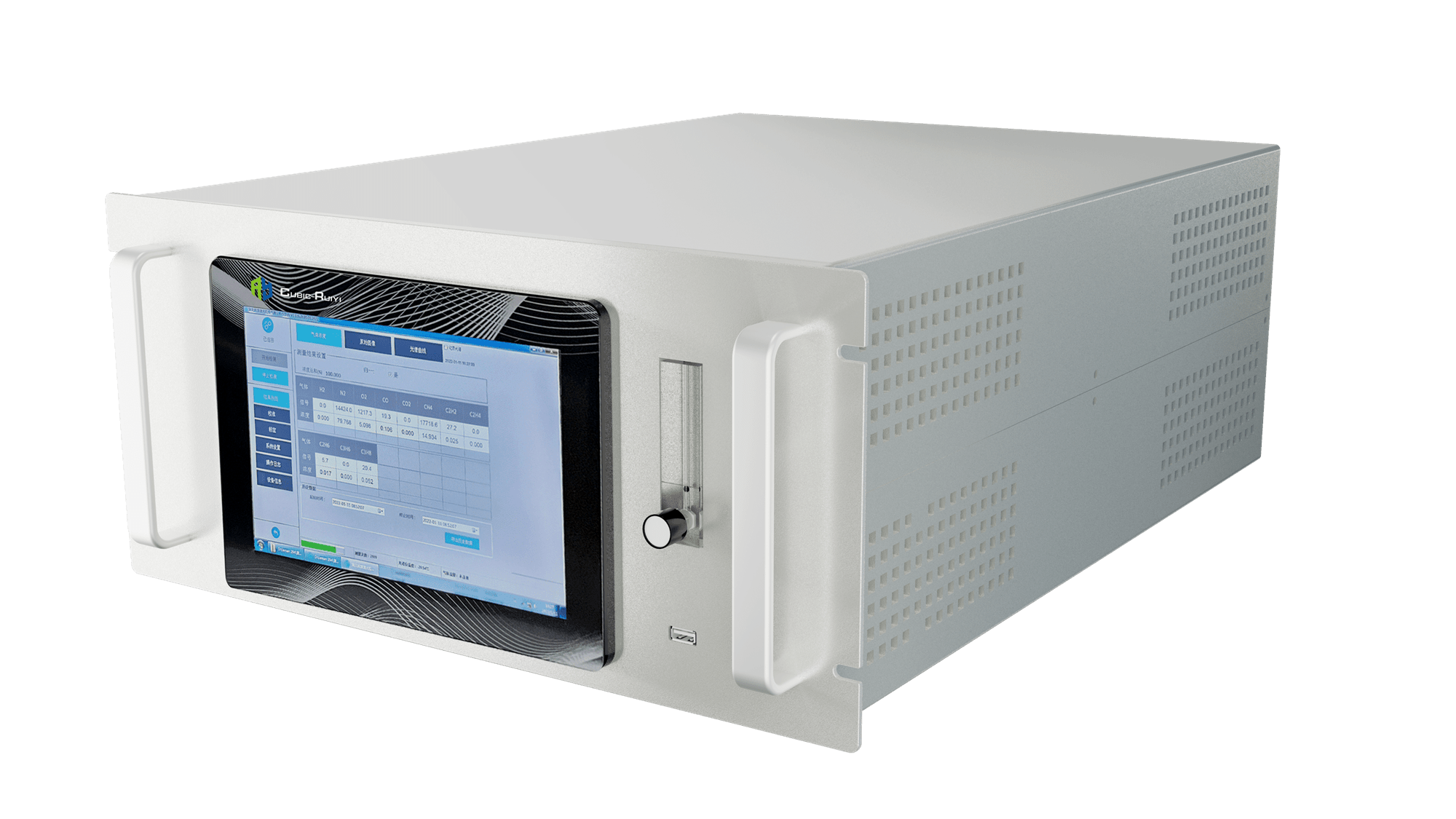

Image Credit: Cubic Sensor and Instrument Co. Ltd
The Cubic LRGA-3100 enables online automated measurement of various combustible components in real-time, including H2, O2, N2, methane, and other hydrocarbons.
Applying LRGA-3100 significantly reduces measurement errors and labor costs associated with manual operations through traditional GC-MS methods.
It also offers high-precision measurements with extremely low drift, ensuring reliable data for the real-time monitoring of natural gas composition and calorific value. Additionally, the ability to adjust the upstream production process based on real-time data changes enhances production efficiency.
Cubic leverages a variety of mature technology platforms to offer innovative methane gas sensing solutions. These are particularly beneficial for monitoring methane emissions in the oil and gas industry, applicable in both upstream and downstream operations.
Confronting challenges from environmental emissions, safety monitoring, and production optimization in this sector, Cubic remains committed to technological innovation. Cubic continues to focus its efforts in this field, consistently providing qualified and reliable gas sensing solutions.

This information has been sourced, reviewed and adapted from materials provided by Cubic Sensor and Instrument Co. Ltd.
For more information on this source, please visit Cubic Sensor and Instrument Co. Ltd. and feel free to contact us [email protected]