This article delves into the growing prominence of Advanced Driver Assistance Systems (ADAS) and their vital role in enhancing road safety.

Image Credit: Radiant Vision Systems
A growing number of commercial and consumer vehicles now offer various ADAS features, including:
- Adaptive driving beam (ADB) headlamps
- Blind spot detection
- Night vision
- Cross-traffic alerts
- Collision warnings
- Advanced automatic emergency braking
- Driver drowsiness alerts
- Lane departure warnings
- Traffic sign recognition
- Adaptive cruise control
The global market for these features is expanding and is projected to rise at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 9.7%. It is expected to more than double by 2030, increasing from US $30.9 billion in 2022 to US $65.1 billion by 2030.1
Utilizing technologies such as cameras, lidar, radar, and infrared sensing, ADAS can be active (such as automatic braking that stops a car before a potential collision, irrespective of whether the driver brakes in time), or passive (such as displaying warning alerts to the driver).
Certain systems monitor the road and environment surrounding the vehicle, while others focus on the interior. Driver-monitoring systems (DMS) can prevent drivers from falling asleep at the wheel and respond to sudden medical emergencies (such as a heart attack). Occupant monitoring systems (OMS) can ensure the safety of children in the back seat and alert commercial drivers of falling cargo or unauthorized passengers.
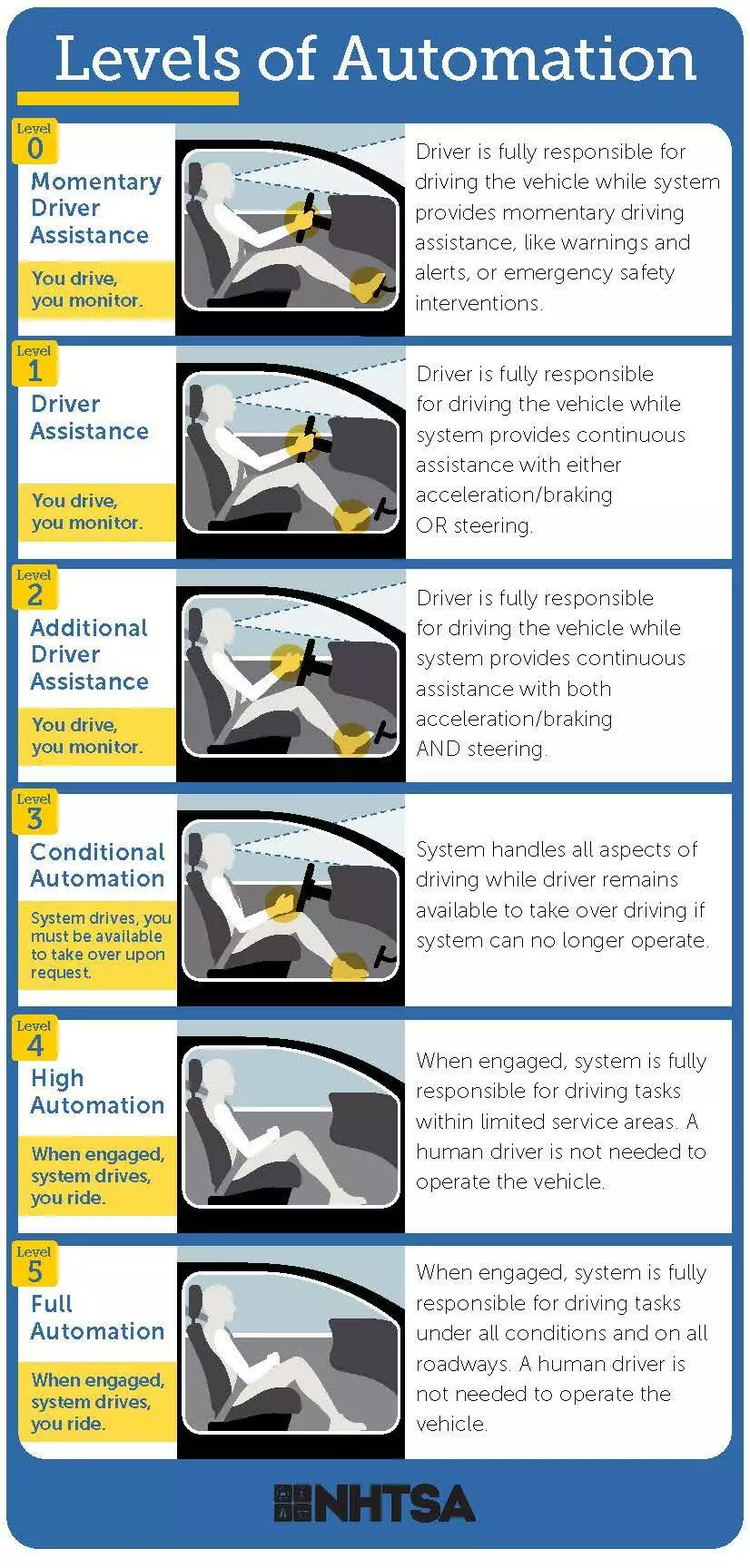
Five levels of vehicle automation, as defined by the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE). (Image Source: NHTSA)
Radiant has worked with automotive customers who develop and implement various ADAS functions and technologies. Radiant’s solutions help Tier suppliers and original equipment manufacturers (OEMs) guarantee the quality and performance of systems utilizing near-infrared (NIR) sensing, cameras, and more.

This information has been sourced, reviewed and adapted from materials provided by Radiant Vision Systems.
For more information on this source, please visit Radiant Vision Systems.