The most popular application of mass air flow sensors is the analysis of mass flow rates of air for fuel-injected combustion engines. Regardless, mass air flow sensors are utilized in several other industries and areas outside of automotive applications.

 Download the Full eBook Here
Download the Full eBook Here
Mass Air Flow Sensors and Medical Devices
Mass air flow sensors are at the center of a range of medical devices, such as machines for the delivery of anesthesia or ventilators. These air flow sensors are frequently miniaturized, thin-film silicon chips (also known as MEMS sensors) but perform on the same heat-loss concepts that automotive air flow sensors do.1
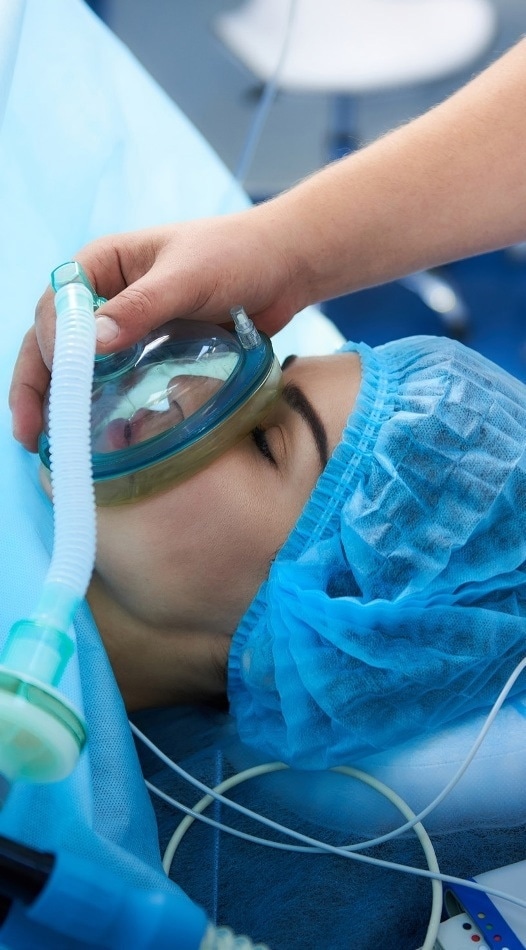
In artificial ventilation devices, precise and consistent monitoring of gas flow rates is needed to mitigate the risk of patient harm from scenarios such as barotrauma, where too much air pressure can result in a rupturing of tissue.2
Here, the sensors need to have a beneficial dynamic range and a quick response time so that even slight fluctuations in flow rate can be compensated for.
Similar air flow sensor devices can also be utilized in gas delivery for sleep apnoea and for anesthesia machines, where the monitoring of gas flow rates leads to the recording of exhalation, and the flow of the machine’s internal blower fan can be decreased in order to best reflect natural breathing patterns.
Analytical Applications of Mass Air Flow Sensors
Mass air flow sensors are also frequently found in analytical chemistry equipment. In gas chromatography, it is one of the most commonly utilized methods for the identification of compounds that are not known.
The air flow sensor traces flow rate information of both the injection process of the sample into the machine and the flow rates through the separation columns. The carrier gas flow rates are critical variables for the total separation time and the resulting chromatography’s quality.3
For gas chromatography it can be beneficial to employ mass flow sensors, rather than volumetric flow, as gas densities vary as a function of temperature. For field instruments that may be vulnerable to extreme environmental fluctuations, this can lead to serious errors in the measurements.4
Mass air flow sensors perform as a key diagnostic on gas chromatography machines, as decreased flow rates can signal blockages in the line or an undesired build-up of contaminants on the column, which could result in decreased sensitivity or the contamination of measurements.

Leak Testing with Air Flow Sensors
By analyzing air flow rates through devices, mass air flow sensors can be utilized to establish not only whether leaks are present, but additionally to characterize the magnitude of the leak.
Using mass air flow sensors in this way is a powerful method appropriate for use in either large or small volumes of gas; therefore, these sensors work with everything from kitchen appliances to huge natural gas pipes.5
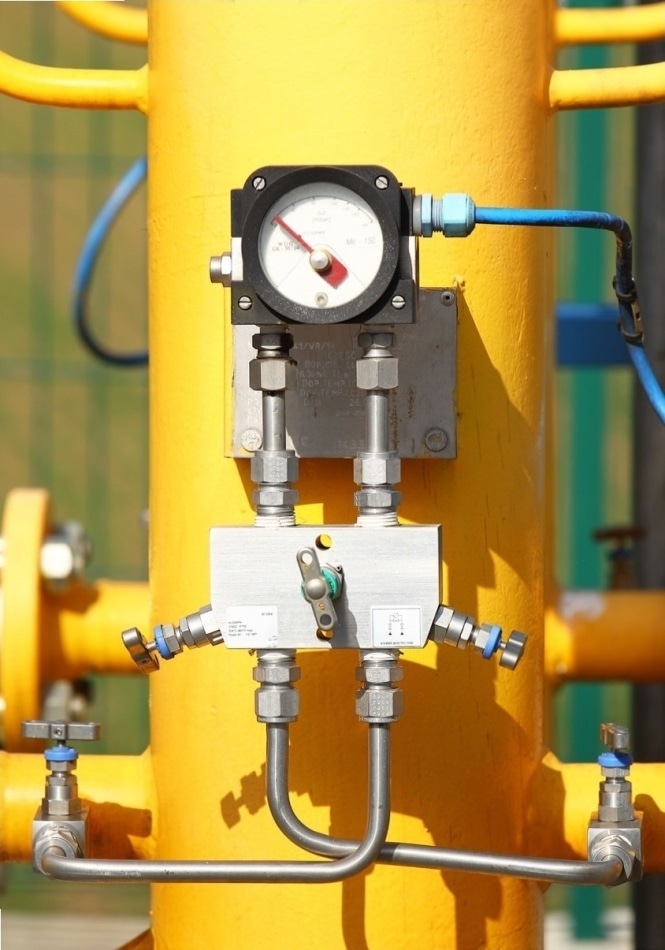

Air flow sensor measures that enable both the quick detection and characterization of the leak size are specifically beneficial when possibly flammable and hazardous gases are involved, as this offers important information for the most efficient and safest response to a leak incident.
Mass air flow based measurements have multiple benefits compared to alternative approaches (for example, pressure-decay leak testing). They are more reliable, with less sensitivity to fluctuating environmental conditions, and do not depend on the calculation of the total volumes of all the parts of the device tested.
This saves a lot of time and takes away one possible source of error.6 Although such air flow sensors are not exactly as inexpensive as pressure-decay devices in terms of the initial investment, their enhanced accuracy, reliability, and decreased measurement times mean that mass air flow leak testers are commonly used.
Heating, ventilation and air conditioning (HVAC) systems now often contain mass air flow sensors as improper air flow settings and the loss of refrigerant gases can both become expensive costs. Monitoring the flow rate output of HVAC systems is also practical in ensuring that buildings have adequate ventilation to keep air quality good.7

Mass Air Flow Sensors in Automotives
Almost all fuel-injection system combustion engines in vehicles contain mass air flow sensors as a feature of their assembly.
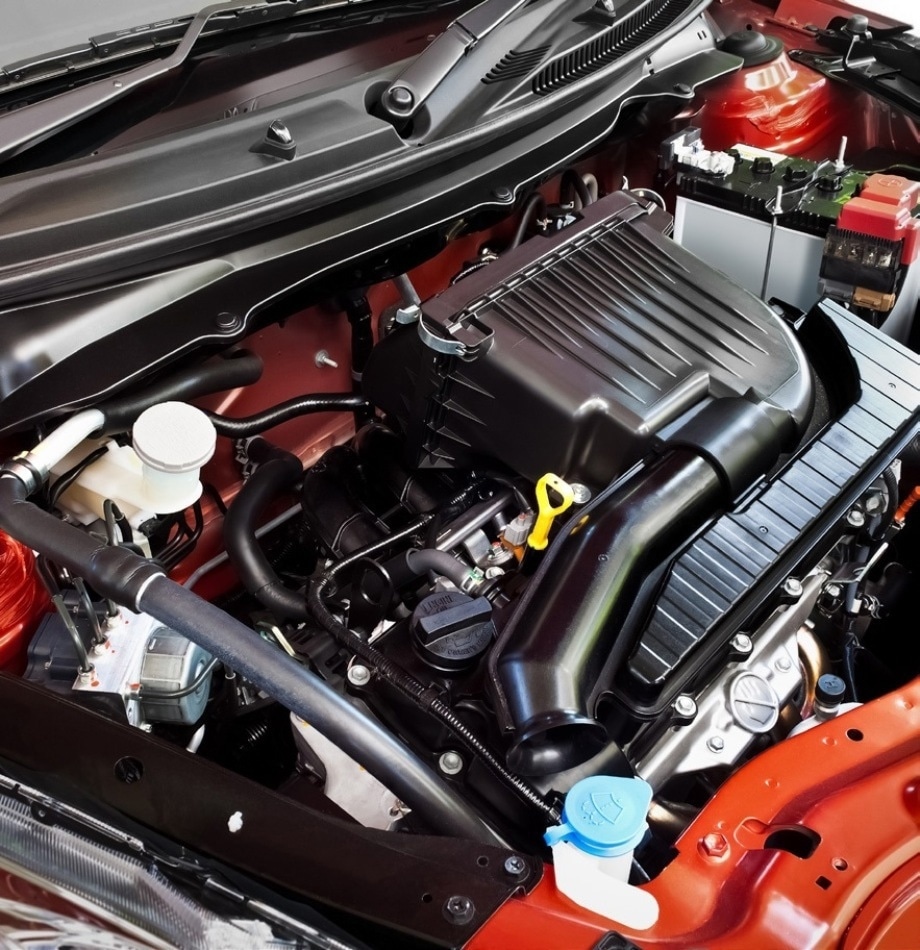

Although types and designs of mass air flow sensors may differ to enhance engine performance under particular conditions, the mass air flow sensor is a critical component in the supply of information to the on-board computer establishing the proper fuel levels to inject to optimize the efficacy of the combustion process.8
Mass air flow sensors play such a crucial role in engine performance, that badly performing sensors can result in completely inaccurate fuel/air ratios that can harm engines, maximize consumption of fuel, and increase the amount of pollutants generated by the vehicle.
Incomplete combustion begins to account for a greater portion of the entire combustion process. If the fuel/air ratio is poor enough, the engine may no longer start due to being very flooded with fuel.
For any applications that depend on particular gas flow rates for functioning, mass air flow sensors are a useful monitoring and diagnostic tool. These kinds of sensors are often simple to connect to data logging and monitoring equipment.
Mass air flow sensors can also be connected to feedback loops to make sure constant mass air flow rates are kept the same, which is highly essential for most of the medical applications of mass air flow sensors.

 Download the Full eBook Here
Download the Full eBook Here
References and Further Reading
Jewitt, H., & Thomas, G. (2012). Measurement of flow and volume of gases. Anaesthesia and Intensive Care Medicine, 13(3), 106–110. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mpaic.2011.12.013
Schena, E., Massaroni, C., Saccomandi, P., & Cecchini, S. (2015). Flow measurement in mechanical ventilation: A review. Medical Engineering and Physics, 37(3), 257–264.
Dömötörová, M., & Matisová, E. (2003). Fast gas chromatography and its use in trace analysis. Journal of Chromatography A, 1000, 199–221.
Chromatography Online, (2019), http://www.chromatographyonline.com
Bergoglio, M., & Mari, D. (2012). Leak rate metrology for the society and industry. Measurement: Journal of the International Measurement Confederation, 45(10), 2434–2440.
Abdulshaheed, A., Mustapha, F., & Ghavamian, A. (2017). A pressure-based method for monitoring leaks in a pipe distribution system: A Review. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 69(May 2015), 902–911. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2016.08.024
Heinemeier, K., Hunt, M., Hoeschele, M., Weitzel, E., & Close, B. (2012). Uncertainties in achieving energy savings from HVAC maintenance measures in the field. ASHRAE Transactions, 118(PART 2), 157–164.
Fleming, W. J. (2008). New Automotive Sensors - A Review. IEEE Sensors Journal, 8(11), 1900–1921.
Disclaimer: The views expressed here are those of the author expressed in their private capacity and do not necessarily represent the views of AZoM.com Limited T/A AZoNetwork the owner and operator of this website. This disclaimer forms part of the Terms and conditions of use of this website.