The rail industry in China is of immense scale by nearly any measure. With a total rail network exceeding 96,000 miles (155,000 km), the country holds the second-largest network globally, alongside the most extensive high-speed rail system spanning over 26,000 miles (42,000 km).
The responsibility of handling almost all rail operations lies with the China Railway Corporation (CRC), which oversees numerous subsidiaries responsible for regional traffic. Together, they operate the world's busiest railways, delivering 3.6 billion passenger trips and transporting 4.4 billion tons of freight annually.
Managing such a crucial long-distance transportation mode necessitates a comprehensive list of priorities. Each railway operator aims to ensure safer and smoother rail operations while effectively managing their assets.
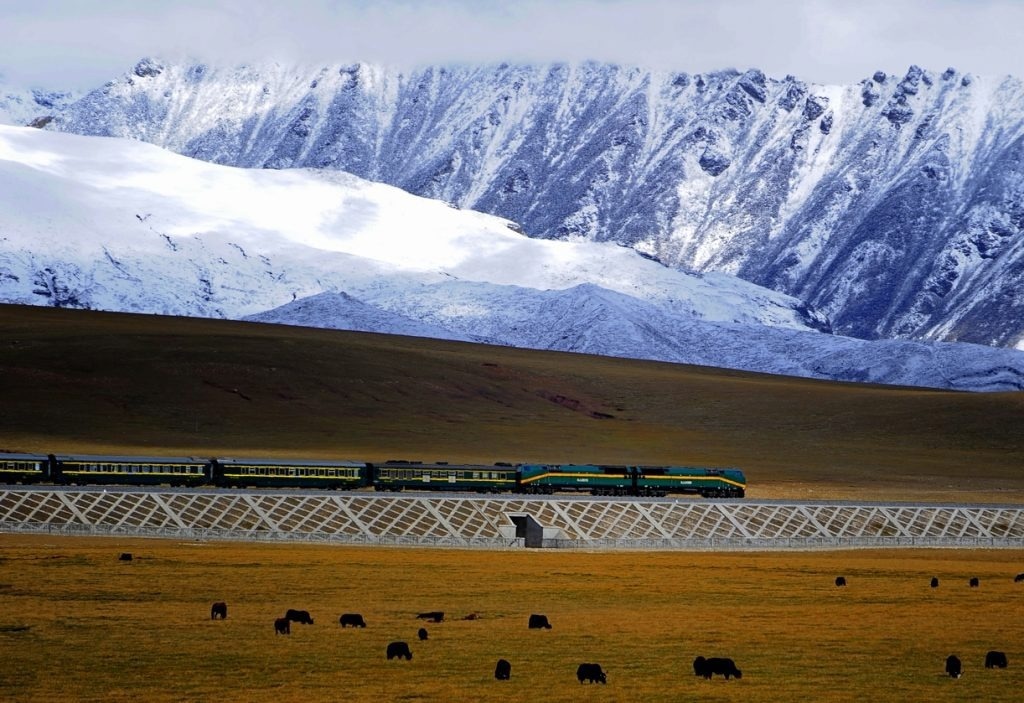

The Qinghai–Tibet railway is a high-elevation railway spanning 1,956 km, connecting Xining, Qinghai Province, to Lhasa, Tibet Autonomous Region of China. Image Credit: Teledyne Judson Technologies
Rail Solutions for a Nation
The China Railway Harbin Group of Technology Corporation (CRTC) is a prominent supplier of rail solutions to Chinese railroad operators. CRTC has been serving industries reliant on rail transport, including agriculture, mining, chemicals, and energy, for over six decades in collaboration with CRC, local metro, and commute railways.
This history is built on a customer-centric approach. Today, this translates into substantial investments in research and development, facilitating the integration of sophisticated systems capable of resolving multiple challenges simultaneously. These systems are expected to be innovative, efficient, reliable, and tailored to specific applications.
This is crucial for a country that experiences significant variations in latitude, longitude, and altitude. Rail lines must tackle the diverse demands of tropical climates in the south, subarctic temperatures in the north, and the formidable elevations of the Tibetan Plateau, among other geographical challenges.
CRTC’s specialization lies in three distinct aspects of rail management:
- Asset management: CRTC offers railway operators a comprehensive database of dynamic measurements, enabling them to detect train conditions and monitor the infrastructure. This advanced system aids in predicting potential railroad accidents and increasing awareness of risks.
- Depot and yard digitalization: With integrating emerging digital technologies, CRTC has successfully transformed depot workshops into intelligent hubs. These upgraded facilities now provide efficient and condition-based services, such as railcar repair, maintenance, and sorting.
- Signaling solutions: Through its reliable axle counting systems, CRTC equips railway operators with accurate load information across extensive track sections, ensuring the smooth operation of their networks.
Safety Solutions with Hot Box Detectors
One of CRTC's primary areas of expertise lies in wayside detection systems for monitoring train conditions. Automated solutions are crucial in ensuring safety due to the vast rail network and constant traffic.
6000 CRTC hot box detectors have been installed on over 2000 rail sites across China. Image Credit: Teledyne Judson Technologies
The flagship product of CRTC is the Hot Box Detector (HBD), making them the leading producer in the country. CRTC's HBDs are vital in safeguarding train operations by generating predictive alarms for CTC managers and rail operators.
These alarms help detect and trace unusually hot axle bearings, preventing failures during subsequent trips across the train fleet.
To facilitate condition-based maintenance, integrated data management systems share this information across different locations, allowing prompt and necessary maintenance at the nearest depot. The system's responsiveness ensures minimal downtime.
How Infrared Imaging Makes Better Solutions Possible
Infrared imaging is a critical component of modern HBDs. Initially, CRTC utilized thermistor detectors for infrared sensing. While these detectors performed well under normal conditions, deviations quickly affected their reliability.
The dynamic environment of a moving train introduced various sources of interference, such as sunlight or the impact of applied wheel braking under specific circumstances.
This issue became especially problematic with the rise of high-speed trains. The response time of a thermistor detector, at the millisecond level, proved too slow to detect hot axles on trains moving at speeds exceeding 160 km/h.
Recognizing the need for a faster and isolated solution, CRTC upgraded its hot box detectors in 2008. They opted to equip their detectors with MCT infrared detectors supplied by Judson Technologies.
These new detectors could operate reliably in temperatures as low as minus 50-60 degrees Celsius, without being affected by ambient conditions.
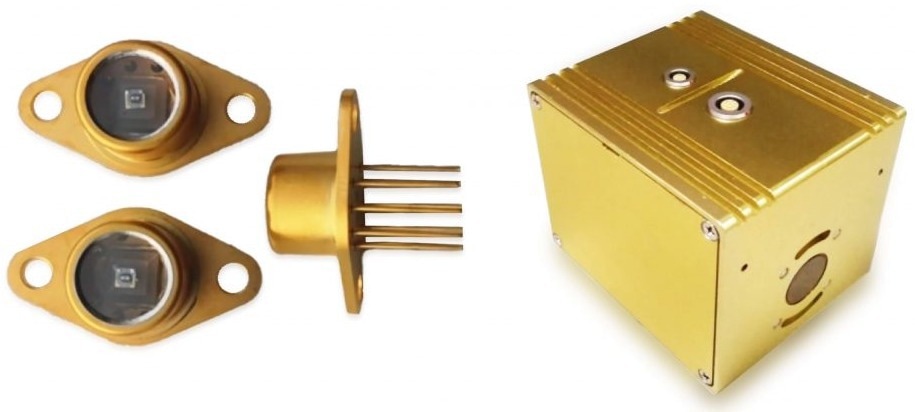

Teledyne Jusdon’s MCT infrared detector (left) and the CRTC scanner unit in which the MCT detector is assembled (right). Image Credit: Teledyne Judson Technologies
To ensure reliable and accurate temperature measurement of each axle bearing, the HBD system needed the capability to precisely determine the source of captured infrared energy.
To address this requirement, CRTC developed a self-adapting software and hardware solution that empowered its HBDs to recognize and differentiate patterns of infrared energy. This innovative solution effectively filters out interference, allowing the system to focus solely on the heat emitted by the axle bearing itself.
As a result, false alarms are significantly reduced, and maintenance efforts are optimized for greater efficiency. A crucial element in this solution was the high-speed response of the new MCT thermal detectors. CRTC's self-adapting approach demanded rapid identification of the appropriate heat patterns while filtering out unwanted interferences.
The resulting system was much faster, achieving microsecond-level performance, a thousand times faster than the previous thermistor sensor and competing infrared solutions based on LiTaO3. The HBD solution successfully detects high-speed trains traveling up to 360 km/h.
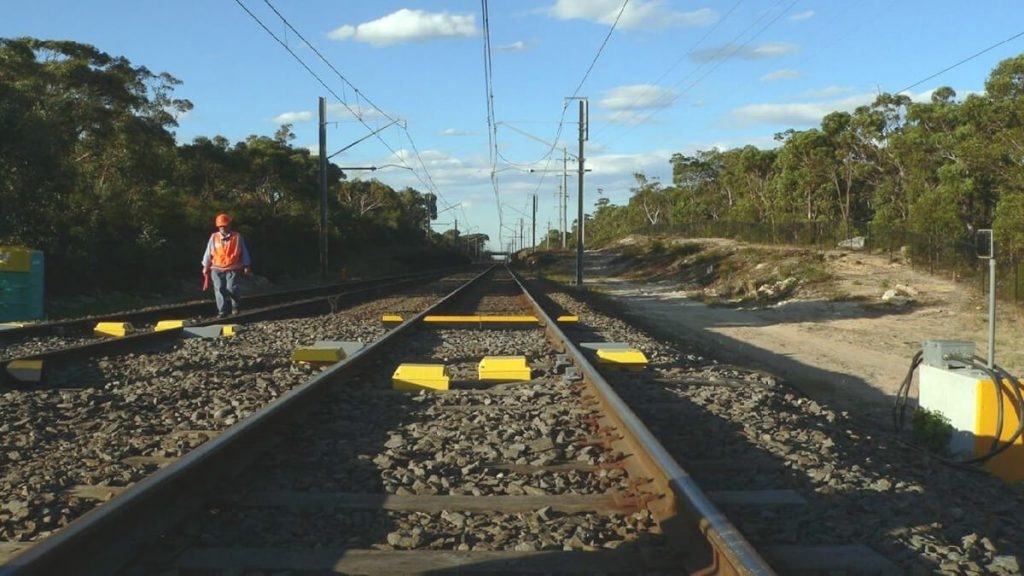

A double-line site of Sydney Trains in NSW, Australia, where CRTC’s HBDs were installed. Image Credit: Teledyne Judson Technologies
Expanding Efficiencies to a Much Wider Network
The CRC has installed over 6000 of these advanced HBDs throughout the national rail network. Of more than one billion rail trips, only a few dozen hot axle bearings instances are detected yearly.
Remarkably, no accidents attributed to hot axles have been reported in recent years, significantly contributing to the safe, reliable, and efficient operation of the Chinese railway network.
While CRC's subsidiaries continue to be CRTC's primary customers, other networks are taking notice of the system's effectiveness. Transnet of South Africa and Sydney Trains of Australia, among others, have become new customers, adopting the same HBDs to enhance the performance of their respective networks.

This information has been sourced, reviewed and adapted from materials provided by Teledyne Judson Technologies.
For more information on this source, please visit Teledyne Judson Technologies.