Gas detectors are usually categorized into three distinct groups for placement:
Plant Protection - Flammable gas detectors are typically categorised into this group. Besides asphyxiation, flammable gases are generally not directly toxic and therefore, the strategic position of detectors is where the gas is expected to accumulate based on its relative density to air (heavier or lighter).
Process Monitoring – Typically gas detection systems in this section are used to monitor and either alarm or be part of processing control. This could be monitoring VOC (Volatile Organic Compounds) levels pre and post filtering, Solvent Vapour (LEL) monitoring in drying ovens, Ventilation control in Car Parks and building etc. Location of these detectors will usually be based on the individual application, after considering the process, gases or vapours, air movement and temperatures involved. Applications falling into this category usually need a good dialogue between IGD and the plant designers to ensure the best placement of the detectors for them to be highly effective.
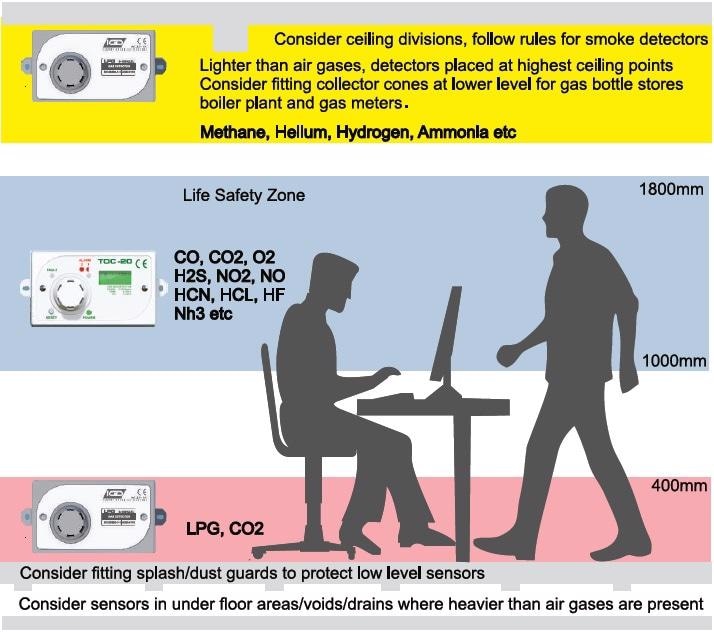
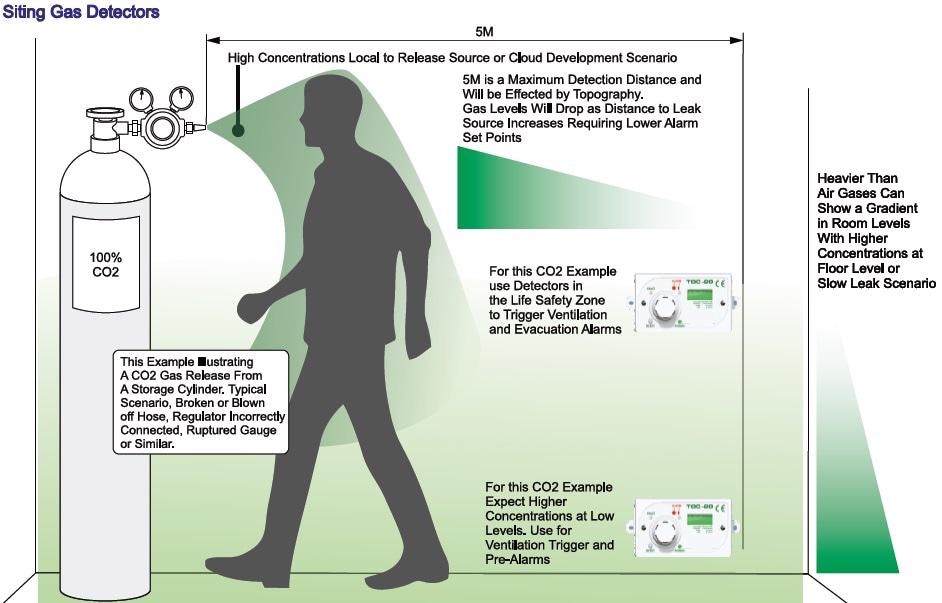
Life Safety Systems – In such systems, the concern is that an asphyxiant or toxic gas is directly hazardous to personnel. The position of the gas detectors is based on the normal operating zone for people in the area of application. It is worth noting at this point that there maybe two sets of detectors involved with a life safety system. The first set of detectors perform as a process monitoring function, with the detection based on the relative density of the gas with respect to the air. This set of detectors is typically used to person some type of function, for example: bringing on extra ventilation to clear a spill hazard.
The second set of detectors are in the ‘life safety or breathing zone’ and alarm for personnel protection. When planning the system, careful consideration needs to be given to the actual setting of alarm levels for the detectors. In general HSE document EH40 lists hazardous gases and vapours and safe occupational exposure limits. IGD base our alarm recommendations on the published figures provided by EH40. Where a detector is fitted into the breathing zone for a gas, which is much heavier than air, then the alarm level is set at a lower level to offset the effect of the higher location.
A typical example would be a Liquid Nitrogen Dewar fill room. In this application we know that spills will occur as Liquid Nitrogen is decanted. In this application the Low-Level Oxygen detectors bring on extra ventilation at ground level to clear the Nitrogen spill as it evaporates into the atmosphere. If the ventilation cannot effectively clear the spill, then the detectors in the breathing zone are used to alarm and evacuate personnel in the area, until such time that the atmosphere returns to normal safe levels.
Specialised Sampling Gas Detectors
As well as manufacturing diffusion based fixed gas detectors, IGD also produce a range of sampling gas detectors. These are utilised where it may be difficult or impractical to use a standard gas detector. Typical applications could be: hard to access areas due to height, accessibility or detector size; clean rooms; where it is desirable to minimise surface areas inside the facility. IGD’s sampling gas detectors are addressable modules that can be fitted alongside standard diffusion type detectors. These sample modules operate continuously using IGD’s piezo pump technology. This technology has virtually no moving parts for enhanced reliability over standard pumps. In addition, the units can be set up to continuously check and correct their zero or calibration point (depending on detector) by drawing a clean filter air sample through a separate port. A diffusion based detector directly in the area of interest is always the best option, where it is required IGD’s sampler modules offer an excellent alternative solution.

Cryogenic Gas Detection
Careful consideration is required for gas detection for applications involving the use of cryogenically cooled gases such as liquid helium or nitrogen. On initial release, cryogenically cooled gases can typically have a lower temperature and higher density compared to their surroundings and therefore, they will have a different behaviour than their gaseous state. In this instance it should be considered for two sets of detection for optimal safety, one for low level detection in the gases cooled state and one for the life safety zone. It is recommended to survey applications involving such gases.
Area Coverage for Gas Detectors
Like smoke detectors, a gas detector is capable of providing up to 75SQ M area coverage based on a 5M radius of operation. There are many factors affecting this, ventilation air flows, gas characteristics, equipment in the area, geometry of a room etc. IGD can provide support throughout the survey, design and installation process to ensure the best possible result on site.

Calibration and Service Requirements for Gas Detection Systems
Regular checking and calibration in compliance with the UK factories Act 1961 and BS EN 60079-29-2:2007 (in the near future Toxic Gas Detection will have a legal requirement to be serviced on a regular bases) is required for all gas detection systems. The service and calibration period will be a function of the application based on environmental in-service conditions. Both IGD and BS EN 60079-29-2:2007 legislation states that gas detection systems must be serviced every 6 months. Furthermore, the PUWER 1998(Provision & Use of Work Equipment Regulation) states “safety equipment needs to be effective and maintained”. With these Acts/Articles in mind, it is essential to ensure that a service plan is in place for any gas detection system deployed as part of a site safety system. IGD can work with operators to offer advice, service and spares to ensure an appropriate level of cover.
Service Engineer Competency: IGD Run an approved engineer training scheme and strongly recommends that only IGD certified engineers who have passed the IGD Engineer training scheme should service and calibrate IGD equipment. IGD offer 12-month or 24 Month service contracts (2 service visits a year). IGD certified engineers will carry the below emblem with a unique number, please consult IGD for proof of competency.

Siting System Components
Control Panels
Control panels should be positioned outside of the hazardous area, protected by their connected gas detectors. They should be accessible such that when an alarm is triggered, it should be possible to evacuate the area and view the gas levels from the controller.
Consider the application of HMI panels, mimic panels or GSM options supplied by IGD to provide additional remote indication/alarm, through email and text notifications.

Audio-Visual Alarms
Related Stories
As a general rule, if there is a gas detection fitted to an area then there should be an audio-visual alarm (beacon sounder) to alert personnel who may be in the same area. Audio-visual alarms are typically standard beacon sounders where the sounder can be silenced from the control panel once an alarm is accepted. IGD offers Standard LED beacon sounder modules, which can be operated from addressable I/O points to minimize cabling. Fitting IGD's range of annunciators is the other option available.

Annunciators
Annunciators are addressable devices usually installed at door entry points. In the event of a gas alarm, a clear audible visual alarm is provided by an annunciator to warn people from entering an area where a gas hazard could be present.

Annunciators are advantageous in many ways when compared to standard beacon sounders. They can be installed on standard dado trunking systems; cannot be confused with other alarms; can be fitted with slam switches; and the displayed alarm message and flashing colour display are unambiguous.
Gas Collector Cones and Splash Guards
Gas collector cones can be considered for use in areas where detectors are placed above gas plant such as boilers or meters in rooms with high ceilings. They are fitted to detectors located just above gas plant to enhance the capability of detectors to sense gas leaks.

Detectors fitted with gas collector cone.
For detectors fitted at low level, fitting splash guards may be appropriate to protect sensors from floor washing, rain splash, dust etc.

ATEX detector with splash guard.

Gas collector hood above valve stations.

This information has been sourced, reviewed and adapted from materials provided by International Gas Detectors Ltd.
For more information on this source, please visit International Gas Detectors Ltd.