University of Cincinnati researchers have come up with a sensor that can rapidly detect dangerous Heavy Metal levels in human beings. The sensor that they have created provides fast feedback to the presence of heavy metals in general and manganese in particular.
The work of the scientists has been published in the August edition of the international journal known as Biomedical Microdevices. The low cost, disposable ‘lab-on-a-chip’ sensor is useful to detect highly electro-negative heavy metals. It performs this function faster than the traditional technology used in health care settings.
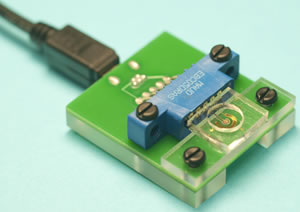 Sensor Promises Rapid Detection of Dangerous Heavy Metal Levels in Humans. Image Credit: University of Cincinnati
Sensor Promises Rapid Detection of Dangerous Heavy Metal Levels in Humans. Image Credit: University of Cincinnati
The new University of Cincinnati sensor technology can be used successfully in point of care devices that need to provide feedback about heavy metal levels within ten minutes. The sensor has wide scale potential for use in clinical, occupational and research settings.
Ian Papautsky, a researcher with the University of Cincinnati said that the conventional methods for measuring manganese levels in blood currently requires about five millilitres of whole blood sent to a lab, with results back in 48 hours.
For a clinician monitoring health effects by measuring these levels in a patient’s blood where a small level of manganese is normal and necessary for metabolic functions you want an answer much more quickly about exposure levels, especially in a rural, high-risk area where access to a certified metals lab is limited. He said that their sensor will only require about two droplets of blood serum and will provide results in about ten minutes. It’s portable and usable anywhere.